Wind Load Resistance

Buildings are constantly exposed to certain loads due to physical and climatic conditions. The most important of these loads and the one that has the highest impact on windows is wind load. Wind load varies as follows depending on the height and type of the building:
| Height Above The Ground (m) | Wind Speed (m/s) | Overall Structure Wind Load Rating (Pa) | Tower Structure Wind Load Rating (Pa) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 - 8 | 28 | 600 | 800 |
| 9 -20 | 36 | 960 | 1280 |
| 21 -100 | 42 | 1320 | 1760 |
| > 100 | 46 | 1560 | 2080 |
* The facade height must be at least 5 times the average building width for a building to be considered as tower type.
* The table values are multiplied by the Sinx value to find the wind load values for surfaces inclined to the wind direction at X angle.
The wind loads to which the windows are exposed are determined as follows according to TS 498 standard.
W = Cf.q (kN/m2)
W : Wind load value
Cf : Aerodynamic load coefficient (the determination of the load coefficient depends on the building geometry and wind direction)
q : Suction velocity pressure (q = v2/1600)
V : Wind speed (m/sec)
There is an inertia caused by the wind loads to which the structures are exposed. This inertia value is calculated using the following formula.
The moment of inertia of the window shall provide the required moment of inertia value calculated in the above formula when calculating the wind load. Thus, the window will be able withstand the resistance caused by the wind load. The inertia value of the profile and reinforcement steel shall be calculated when calculating the inertia value of the window to find the required inertia value. The thickness and shape of the reinforcement steel to be used are determined according to this calculation.
The window dimensions and the types of reinforcement steel to be used are determined on the basis of the calculations of average wind load of the region and inertia.
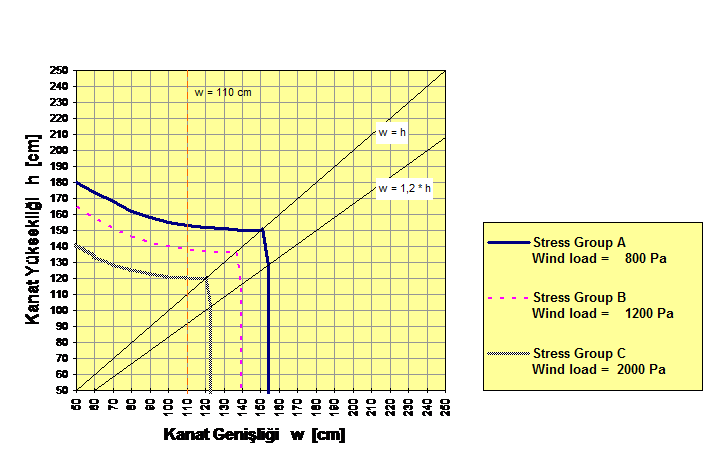
Sash Height h (cm)
Sash Width w (cm)